What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs if the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the brain is blocked. Without oxygen, brain cells start to die after a few minutes. Sudden bleeding in the brain also can cause a stroke if it damages brain cells.
If brain cells die or are damaged because of a stroke, symptoms occur in the parts of the body that these brain cells control. Examples of stroke symptoms include sudden weakness; paralysis or numbness of the face, arms, or legs (paralysis is an inability to move); trouble speaking or understanding speech; and trouble seeing.
A stroke is a serious medical condition that requires emergency care. A stroke can cause lasting brain damage, long-term disability, or even death.
If you think you or someone else is having a stroke, call 9–1–1 right away. Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. Call an ambulance so that medical personnel can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the emergency room. During a stroke, every minute counts.
Outlook
Stroke is a leading cause of death in the United States. Many factors can raise your risk of having a stroke. Talk with your doctor about how you can control these risk factors and help prevent a stroke.
If you have a stroke, prompt treatment can reduce damage to your brain and help you avoid lasting disabilities. Prompt treatment also may help prevent another stroke.
Researchers continue to study the causes and risk factors for stroke. They’re also finding new and better treatments and new ways to help the brain repair itself after a stroke.
If you think someone is having a stroke, the National Stroke Association wants you to act FAST. Remember:
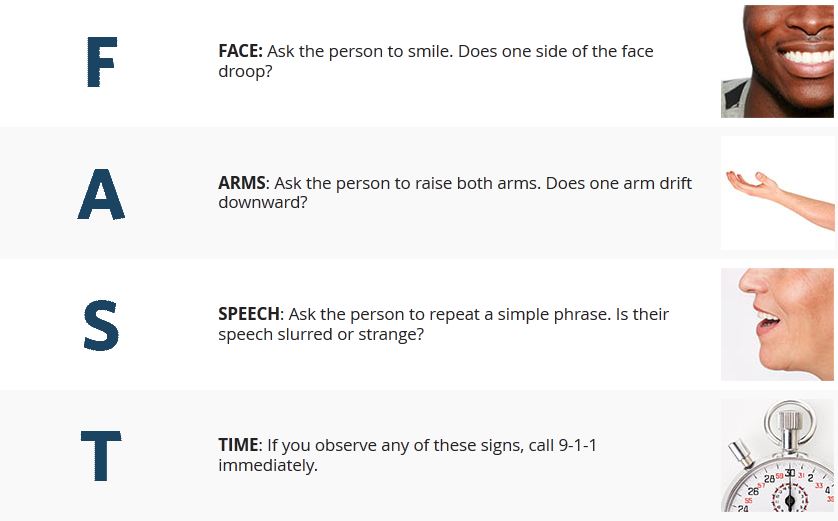
If a person is exhibiting one or more of these signs, call 9-1-1 immediately.
Content provided by the website for the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov)